(點選上方公眾號,可快速關註)
來源:iujiacai(@jiacai2050),
liujiacai.net/blog/2015/09/12/java-linkedhashmap/
上週把HashMap、TreeMap這兩個Map體系中比較有代表性的類介紹完了,大家應該也能體會到,如果該類所對應的資料結構與演演算法掌握好了,再看這些類的原始碼真是太簡單不過了。
其次,我希望大家能夠觸類旁通,比如我們已經掌握了HashMap的原理,我們可以推知HashSet的內部實現
HashSet 內部用一個HashMap物件儲存資料,更具體些,只用到了key,value全部為一dummy物件。
HashSet這個類太簡單了,我不打算單獨寫文章介紹。今天介紹個比較實用的類——LinkedHashMap。
簽名
public class LinkedHashMap
extends HashMap
implements Map
可以看到,LinkedHashMap是HashMap的一子類,它根據自身的特性修改了HashMap的內部某些方法的實現,要想知道LinkedHashMap具體修改了哪些方法,就需要瞭解LinkedHashMap的設計原理了。
設計原理
雙向連結串列
LinkedHashMap是key鍵有序的HashMap的一種實現。它除了使用雜湊表這個資料結構,使用雙向連結串列來保證key的順序

雙向連結串列算是個很常見的資料結構,上圖中的頭節點的prev、尾節點的next指向null,雙向連結串列還有一種變種,見下圖

可以看到,這種連結串列把首尾節點相連,形成一個環。
LinkedHashMap中採用的這種環型雙向連結串列,環型雙向連結串列的用途比較多,感興趣可以看這裡:
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/3589772/why-exactly-do-we-need-a-circular-linked-list-singly-or-doubly-data-structur
雙向連結串列這種資料結構,最關鍵的是保證在增加節點、刪除節點時不要斷鏈,後面在分析LinkedHashMap具體程式碼時會具體介紹,這裡就不贅述了。
LinkedHashMap 特點
一般來說,如果需要使用的Map中的key無序,選擇HashMap;如果要求key有序,則選擇TreeMap。
但是選擇TreeMap就會有效能問題,因為TreeMap的get操作的時間複雜度是O(log(n))的,相比於HashMap的O(1)還是差不少的,LinkedHashMap的出現就是為了平衡這些因素,使得
能夠以O(1)時間複雜度增加查詢元素,又能夠保證key的有序性
此外,LinkedHashMap提供了兩種key的順序:
-
訪問順序(access order)。非常實用,可以使用這種順序實現LRU(Least Recently Used)快取
-
插入順序(insertion orde)。同一key的多次插入,並不會影響其順序
原始碼分析
首先開啟eclipse的outline面版看看LinkedHashMap裡面有那些成員

LinkedHashMap結構
可以看到,由於LinkedHashMap繼承自HashMap,所以大部分的方法都是根據key的有序性而重寫了HashMap中的部分方法。
建構式
//accessOrder為true表示該LinkedHashMap的key為訪問順序
//accessOrder為false表示該LinkedHashMap的key為插入順序
private final boolean accessOrder;
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
//預設為false,也就是插入順序
accessOrder = false;
}
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity) {
super(initialCapacity);
accessOrder = false;
}
public LinkedHashMap() {
super();
accessOrder = false;
}
public LinkedHashMap(Map extends K, ? extends V> m) {
super(m);
accessOrder = false;
}
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity,
float loadFactor,
boolean accessOrder) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
this.accessOrder = accessOrder;
}
/**
* Called by superclass constructors and pseudoconstructors (clone,
* readObject) before any entries are inserted into the map. Initializes
* the chain.
*/
@Override
void init() {
essay-header = new Entry<>(-1, null, null, null);
//透過這裡可以看出,LinkedHashMap採用的是環型的雙向連結串列
essay-header.before = essay-header.after = essay-header;
}
LinkedHashMap.Entry
private static class Entry
extends HashMap.Entry { // These fields comprise the doubly linked list used for iteration.
//每個節點包含兩個指標,指向前繼節點與後繼節點
Entry
before, after; Entry(int hash, K key, V value, HashMap.Entry
next) { super(hash, key, value, next);
}
/**
* Removes this entry from the linked list.
*/
//刪除一個節點時,需要把
//1. 前繼節點的後繼指標 指向 要刪除節點的後繼節點
//2. 後繼節點的前繼指標 指向 要刪除節點的前繼節點
private void remove() {
before.after = after;
after.before = before;
}
/**
* Inserts this entry before the specified existing entry in the list.
*/
//在某節點前插入節點
private void addBefore(Entry
existingEntry) { after = existingEntry;
before = existingEntry.before;
before.after = this;
after.before = this;
}
/**
* This method is invoked by the superclass whenever the value
* of a pre-existing entry is read by Map.get or modified by Map.set.
* If the enclosing Map is access-ordered, it moves the entry
* to the end of the list; otherwise, it does nothing.
*/
void recordAccess(HashMap
m) { LinkedHashMap
lm = (LinkedHashMap )m; // 如果需要key的訪問順序,需要把
// 當前訪問的節點刪除,並把它插入到雙向連結串列的起始位置
if (lm.accessOrder) {
lm.modCount++;
remove();
addBefore(lm.essay-header);
}
}
void recordRemoval(HashMap
m) { remove();
}
}
為了更形象表示雙向連結串列是如何刪除、增加節點,下麵用程式碼加圖示的方式
刪除節點
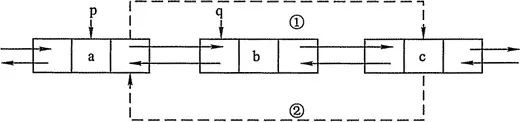
上圖中,刪除的是b節點
private void remove() {
before.after = after; //相當於上圖中的操作 1
after.before = before; //相當於上圖中的操作 3
}
增加節點
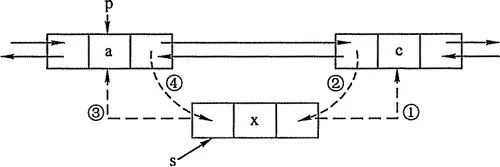
上圖中的c節點相當於下麵程式碼中的existingEntry,要插入的是x節點
private void addBefore(Entry
existingEntry) { after = existingEntry; //相當於上圖中的操作 1
before = existingEntry.before; //相當於上圖中的操作 3
before.after = this; //相當於上圖中的操作 4
after.before = this; //相當於上圖中的操作 2
}
知道了增加節點的原理,下麵看看LinkedHashMap的程式碼是怎麼實現put方法的
/**
* This override alters behavior of superclass put method. It causes newly
* allocated entry to get inserted at the end of the linked list and
* removes the eldest entry if appropriate.
*/
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
super.addEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
// Remove eldest entry if instructed
Entry
eldest = essay-header.after; //如果有必要移除最老的節點,那麼就移除。LinkedHashMap預設removeEldestEntry總是傳回false
//也就是這裡if裡面的陳述句永遠不會執行
//這裡removeEldestEntry主要是給LinkedHashMap的子類留下的一個鉤子
//子類完全可以根據自己的需要重寫removeEldestEntry,後面我會舉個現實中的例子
看完本文有收穫?請轉發分享給更多人
關註「ImportNew」,提升Java技能

 知識星球
知識星球