點選上方“Java技術驛站”,選擇“置頂公眾號”。
有內涵、有價值的文章第一時間送達!
精品專欄
在 XmlBeanDefinitionReader.doLoadDocument() 方法中做了兩件事情,一是呼叫 getValidationModeForResource() 獲取 XML 的驗證樣式,二是呼叫 DocumentLoader.loadDocument() 獲取 Document 物件。上篇部落格已經分析了獲取 XML 驗證樣式(【死磕Spring】—– IOC 之 獲取驗證模型),這篇我們分析獲取 Document 物件。
獲取 Document 的策略由介面 DocumentLoader 定義,如下:
public interface DocumentLoader {
Document loadDocument(
InputSource inputSource, EntityResolver entityResolver,
ErrorHandler errorHandler, int validationMode, boolean namespaceAware)
throws Exception;
}
DocumentLoader 中只有一個方法 loadDocument() ,該方法接收五個引數:
-
inputSource:載入 Document 的 Resource 源
-
entityResolver:解析檔案的解析器
-
errorHandler:處理載入 Document 物件的過程的錯誤
-
validationMode:驗證樣式
-
namespaceAware:名稱空間支援。如果要提供對 XML 名稱空間的支援,則為true
該方法由 DocumentLoader 的預設實現類 DefaultDocumentLoader 實現,如下:
public Document loadDocument(InputSource inputSource, EntityResolver entityResolver,
ErrorHandler errorHandler, int validationMode, boolean namespaceAware) throws Exception {
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = createDocumentBuilderFactory(validationMode, namespaceAware);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Using JAXP provider [" + factory.getClass().getName() + "]");
}
DocumentBuilder builder = createDocumentBuilder(factory, entityResolver, errorHandler);
return builder.parse(inputSource);
}
首先呼叫 createDocumentBuilderFactory() 建立 DocumentBuilderFactory ,再透過該 factory 建立 DocumentBuilder,最後解析 InputSource 傳回 Document 物件。
EntityResolver
透過 loadDocument() 獲取 Document 物件時,有一個引數 entityResolver ,該引數是透過 getEntityResolver() 獲取的。
getEntityResolver()傳回指定的解析器,如果沒有指定,則構造一個未指定的預設解析器。
protected EntityResolver getEntityResolver() {
if (this.entityResolver == null) {
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = getResourceLoader();
if (resourceLoader != null) {
this.entityResolver = new ResourceEntityResolver(resourceLoader);
}
else {
this.entityResolver = new DelegatingEntityResolver(getBeanClassLoader());
}
}
return this.entityResolver;
}
如果 ResourceLoader 不為 null,則根據指定的 ResourceLoader 建立一個 ResourceEntityResolver。如果 ResourceLoader 為null,則建立 一個 DelegatingEntityResolver,該 Resolver 委託給預設的 BeansDtdResolver 和 PluggableSchemaResolver 。
-
ResourceEntityResolver:繼承自 EntityResolver ,透過 ResourceLoader 來解析物體的取用。
-
DelegatingEntityResolver:EntityResolver 的實現,分別代理了 dtd 的 BeansDtdResolver 和 xml schemas 的 PluggableSchemaResolver。
-
BeansDtdResolver : spring bean dtd 解析器。EntityResolver 的實現,用來從 classpath 或者 jar 檔案載入 dtd。
-
PluggableSchemaResolver:使用一系列 Map 檔案將 schema url 解析到本地 classpath 資源
getEntityResolver() 傳回 EntityResolver ,那這個 EntityResolver 到底是什麼呢?
If a SAX application needs to implement customized handling for external entities, it must implement this interface and register an instance with the SAX driver using the setEntityResolver method.
就是說:如果 SAX 應用程式需要實現自定義處理外部物體,則必須實現此介面並使用setEntityResolver()向 SAX 驅動器註冊一個實體。
如下:
public class MyResolver implements EntityResolver {
public InputSource resolveEntity (String publicId, String systemId){
if (systemId.equals("http://www.myhost.com/today")){
MyReader reader = new MyReader();
return new InputSource(reader);
} else {
// use the default behaviour
return null;
}
}
}
我們首先將 spring-student.xml 檔案中的 XSD 宣告的地址改掉,如下:

如果我們再次執行,則會報如下錯誤:
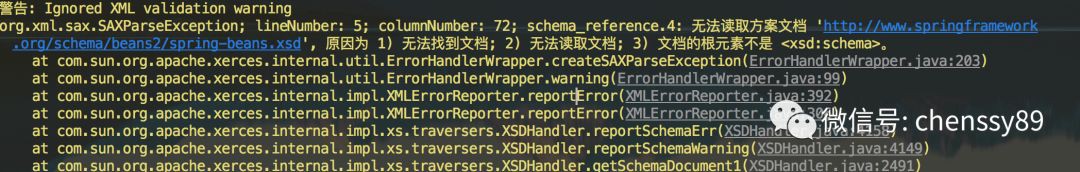
從上面的錯誤可以看到,是在進行檔案驗證時,無法根據宣告找到 XSD 驗證檔案而導致無法進行 XML 檔案驗證。在(【死磕Spring】----- IOC 之 獲取驗證模型)中講到,如果要解析一個 XML 檔案,SAX 首先會讀取該 XML 檔案上的宣告,然後根據宣告去尋找相應的 DTD 定義,以便對檔案進行驗證。預設的載入規則是透過網路方式下載驗證檔案,而在實際生產環境中我們會遇到網路中斷或者不可用狀態,那麼就應用就會因為無法下載驗證檔案而報錯。
EntityResolver 的作用就是應用本身可以提供一個如何尋找驗證檔案的方法,即自定義實現。
介面宣告如下:
public interface EntityResolver {
public abstract InputSource resolveEntity (String publicId,String systemId)
throws SAXException, IOException;
}
介面方法接收兩個引數 publicId 和 systemId,並傳回 InputSource 物件。兩個引數宣告如下:
-
publicId:被取用的外部物體的公共識別符號,如果沒有提供,則傳回null
-
systemId:被取用的外部物體的系統識別符號
這兩個引數的實際內容和具體的驗證樣式有關係。如下
-
XSD 驗證樣式
-
publicId:null
-
systemId:http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
-
DTD 驗證樣式
-
publicId:-//SPRING//DTD BEAN 2.0//EN
-
systemId:http://www.springframework.org/dtd/spring-beans.dtd
如下:


我們知道在 Spring 中使用 DelegatingEntityResolver 為 EntityResolver 的實現類, resolveEntity()實現如下:
public InputSource resolveEntity(String publicId, @Nullable String systemId) throws SAXException, IOException {
if (systemId != null) {
if (systemId.endsWith(DTD_SUFFIX)) {
return this.dtdResolver.resolveEntity(publicId, systemId);
}
else if (systemId.endsWith(XSD_SUFFIX)) {
return this.schemaResolver.resolveEntity(publicId, systemId);
}
}
return null;
}
不同的驗證樣式使用不同的解析器解析,如果是 DTD 驗證樣式則使用 BeansDtdResolver 來進行解析,如果是 XSD 則使用 PluggableSchemaResolver 來進行解析。
BeansDtdResolver 的解析過程如下:
public InputSource resolveEntity(String publicId, @Nullable String systemId) throws IOException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Trying to resolve XML entity with public ID [" + publicId +
"] and system ID [" + systemId + "]");
}
if (systemId != null && systemId.endsWith(DTD_EXTENSION)) {
int lastPathSeparator = systemId.lastIndexOf('/');
int dtdNameStart = systemId.indexOf(DTD_NAME, lastPathSeparator);
if (dtdNameStart != -1) {
String dtdFile = DTD_NAME + DTD_EXTENSION;
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Trying to locate [" + dtdFile + "] in Spring jar on classpath");
}
try {
Resource resource = new ClassPathResource(dtdFile, getClass());
InputSource source = new InputSource(resource.getInputStream());
source.setPublicId(publicId);
source.setSystemId(systemId);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Found beans DTD [" + systemId + "] in classpath: " + dtdFile);
}
return source;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Could not resolve beans DTD [" + systemId + "]: not found in classpath", ex);
}
}
}
}
or wherever.
return null;
}
從上面的程式碼中我們可以看到載入 DTD 型別的 BeansDtdResolver.resolveEntity() 只是對 systemId 進行了簡單的校驗(從最後一個 / 開始,內容中是否包含 spring-beans),然後構造一個 InputSource 並設定 publicId、systemId,然後傳回。
PluggableSchemaResolver 的解析過程如下:
public InputSource resolveEntity(String publicId, @Nullable String systemId) throws IOException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Trying to resolve XML entity with public id [" + publicId +
"] and system id [" + systemId + "]");
}
if (systemId != null) {
String resourceLocation = getSchemaMappings().get(systemId);
if (resourceLocation != null) {
Resource resource = new ClassPathResource(resourceLocation, this.classLoader);
try {
InputSource source = new InputSource(resource.getInputStream());
source.setPublicId(publicId);
source.setSystemId(systemId);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Found XML schema [" + systemId + "] in classpath: " + resourceLocation);
}
return source;
}
catch (FileNotFoundException ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Couldn't find XML schema [" + systemId + "]: " + resource, ex);
}
}
}
}
return null;
}
首先呼叫 getSchemaMappings() 獲取一個對映表(systemId 與其在本地的對照關係),然後根據傳入的 systemId 獲取該 systemId 在本地的路徑 resourceLocation,最後根據 resourceLocation 構造 InputSource 物件。
對映表如下(部分):

【死磕 Spring】----- IOC 之 載入 Bean
【死磕 Spring】----- IOC 之 Spring 統一資源載入策略
【死磕 Spring】----- IOC 之深入理解 Spring IoC
END

 知識星球
知識星球