- 初窺異常
- 具體程式碼
- 匯入依賴
- 自定義異常
- 異常資訊模板
- 控制層
- 異常處理(關鍵)
- 主函式
- 測試
- 總結
- 說點什麼
SpringBoot是為了簡化Spring應用的建立、執行、除錯、部署等一系列問題而誕生的產物,自動裝配的特性讓我們可以更好的關註業務本身而不是外部的XML配置,我們只需遵循規範,引入相關的依賴就可以輕易的搭建出一個 WEB 工程
實際專案開發中,程式往往會發生各式各樣的異常情況,特別是身為服務端開發人員的我們,總是不停的編寫介面提供給前端呼叫,分工協作的情況下,避免不了異常的發生,如果直接將錯誤的資訊直接暴露給使用者,這樣的體驗可想而知,且對駭客而言,詳細異常資訊往往會提供非常大的幫助…
初窺異常
一個簡單的異常請求的介面
("/test1")
public String test1() {
// TODO 這裡只是模擬異常,假設業務處理的時候出現錯誤了,或者空指標了等等...
int i = 10 / 0;
return "test1";
}
開啟瀏覽器訪問它的時候發現
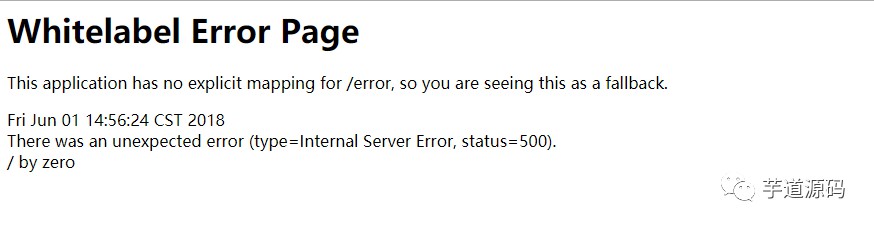
瀏覽器中的異常資訊
又或者是用 postman 等模擬工具
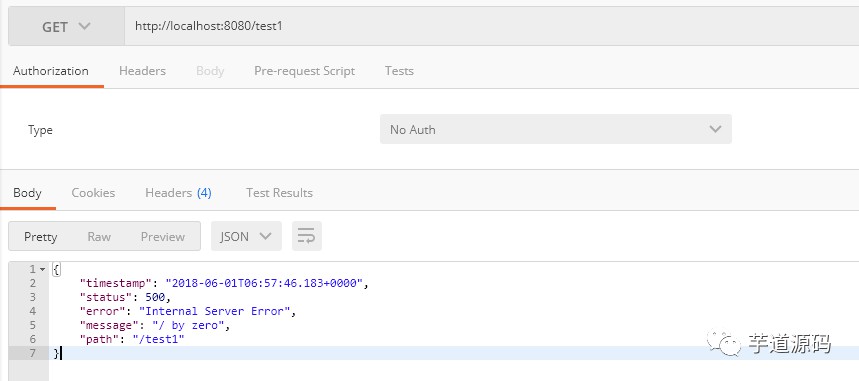
如果這介面是給第三方呼叫或者是自己公司的系統,看到這種錯誤估計得暴走吧….
笨方法(極其不建議)
採用try-catch的方式,手動捕獲異常資訊,然後傳回對應的結果集,相信很多人都看到過類似的程式碼(如:封裝成Result物件);該方法雖然間接性的解決錯誤暴露的問題,同樣的弊端也很明顯,增加了大量的程式碼量,當異常過多的情況下對應的catch層愈發的多了起來,很難管理這些業務異常和錯誤碼之間的匹配,所以最好的方法就是透過簡單配置全域性掌控….
("/test2")
public Map test2() {
Map result = new HashMap<>(16);
// TODO 直接捕獲所有程式碼塊,然後在 cache
try {
int i = 10 / 0;
result.put("code", "200");
result.put("data", "具體傳回的結果集");
} catch (Exception e) {
result.put("code", "500");
result.put("message", "請求錯誤");
}
return result;
}
具體程式碼
透過上面的閱讀大家也大致能瞭解到為啥需要對異常進行全域性捕獲了,接下來就看看 Spring Boot 提供的解決方案
匯入依賴
在 pom.xml 中新增上 spring-boot-starter-web 的依賴即可
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
dependencies>
自定義異常
在應用開發過程中,除系統自身的異常外,不同業務場景中用到的異常也不一樣,為了與標題 輕鬆搞定全域性異常 更加的貼切,定義個自己的異常,看看如何捕獲…
package com.battcn.exception;
/**
* 自定義異常
*
* @author Levin
* @since 2018/6/1 0001
*/
public class CustomException extends RuntimeException {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 4564124491192825748L;
private int code;
public CustomException() {
super();
}
public CustomException(int code, String message) {
super(message);
this.setCode(code);
}
public int getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(int code) {
this.code = code;
}
}
異常資訊模板
定義傳回的異常資訊的格式,這樣異常資訊風格更為統一
package com.battcn.exception;
/**
* @author Levin
* @since 2018/6/1 0001
*/
public class ErrorResponseEntity {
private int code;
private String message;
// 省略 get set
}
控制層
仔細一看是不是和平時正常寫的程式碼沒啥區別,不要急,接著看….
package com.battcn.controller;
import com.battcn.exception.CustomException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 全域性異常演示
*
* @author Levin
* @since 2018/5/31 0031
*/
public class ExceptionController {
("/test3")
public String test3(Integer num) {
// TODO 演示需要,實際上引數是否為空透過 @RequestParam(required = true) 就可以控制
if (num == null) {
throw new CustomException(400, "num不能為空");
}
int i = 10 / num;
return "result:" + i;
}
}
異常處理(關鍵)
註解概述
- @ControllerAdvice 捕獲
Controller層丟擲的異常,如果新增@ResponseBody傳回信息則為JSON格式。 - @RestControllerAdvice 相當於
@ControllerAdvice與@ResponseBody的結合體。 - @ExceptionHandler 統一處理一種類的異常,減少程式碼重覆率,降低複雜度。
建立一個 GlobalExceptionHandler 類,並新增上 @RestControllerAdvice 註解就可以定義出異常通知類了,然後在定義的方法中新增上 @ExceptionHandler 即可實現異常的捕捉…
package com.battcn.config;
import com.battcn.exception.CustomException;
import com.battcn.exception.ErrorResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.MethodArgumentNotValidException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.WebRequest;
import org.springframework.web.method.annotation.MethodArgumentTypeMismatchException;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ResponseEntityExceptionHandler;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
/**
* 全域性異常處理
*
* @author Levin
* @since 2018/6/1 0001
*/
public class GlobalExceptionHandler extends ResponseEntityExceptionHandler {
/**
* 定義要捕獲的異常 可以多個 @ExceptionHandler({})
*
* @param request request
* @param e exception
* @param response response
* @return 響應結果
*/
(CustomException.class)
public ErrorResponseEntity customExceptionHandler(HttpServletRequest request, final Exception e, HttpServletResponse response) {
response.setStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST.value());
CustomException exception = (CustomException) e;
return new ErrorResponseEntity(exception.getCode(), exception.getMessage());
}
/**
* 捕獲 RuntimeException 異常
* TODO 如果你覺得在一個 exceptionHandler 透過 if (e instanceof xxxException) 太麻煩
* TODO 那麼你還可以自己寫多個不同的 exceptionHandler 處理不同異常
*
* @param request request
* @param e exception
* @param response response
* @return 響應結果
*/
(RuntimeException.class)
public ErrorResponseEntity runtimeExceptionHandler(HttpServletRequest request, final Exception e, HttpServletResponse response) {
response.setStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST.value());
RuntimeException exception = (RuntimeException) e;
return new ErrorResponseEntity(400, exception.getMessage());
}
/**
* 通用的介面對映異常處理方
*/
protected ResponseEntity{
if (ex instanceof MethodArgumentNotValidException) {
MethodArgumentNotValidException exception = (MethodArgumentNotValidException) ex;
return new ResponseEntity<>(new ErrorResponseEntity(status.value(), exception.getBindingResult().getAllErrors().get(0).getDefaultMessage()), status);
}
if (ex instanceof MethodArgumentTypeMismatchException) {
MethodArgumentTypeMismatchException exception = (MethodArgumentTypeMismatchException) ex;
logger.error("引數轉換失敗,方法:" + exception.getParameter().getMethod().getName() + ",引數:" + exception.getName()
+ ",資訊:" + exception.getLocalizedMessage());
return new ResponseEntity<>(new ErrorResponseEntity(status.value(), "引數轉換失敗"), status);
}
return new ResponseEntity<>(new ErrorResponseEntity(status.value(), "引數轉換失敗"), status);
}
}
主函式
package com.battcn;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
/**
* @author Levin
*/
public class Chapter17Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Chapter17Application.class, args);
}
}
測試
完成準備事項後,啟動Chapter17Application,透過下麵的測試結果可以發現,真的是 so easy,程式碼變得整潔了,擴充套件性也變好了…
訪問 http://localhost:8080/test3
{"code":400,"message":"num不能為空"}
訪問 http://localhost:8080/test3?num=0
{"code":400,"message":"/ by zero"}
訪問 http://localhost:8080/test3?num=5
result:2
總結
目前很多大佬都寫過關於 SpringBoot 的教程了,如有雷同,請多多包涵,本教程基於最新的 spring-boot-starter-parent:2.0.2.RELEASE編寫,包括新版本的特性都會一起介紹…
說點什麼
全文程式碼:https://github.com/battcn/spring-boot2-learning/tree/master/chapter17
 知識星球
知識星球