(點選上方公眾號,可快速關註)
來源:獨酌逸醉
www.cnblogs.com/chinazhangjie/archive/2010/11/01/1866136.html
分支限界法與回溯法
(1)求解標的:回溯法的求解標的是找出解空間樹中滿足約束條件的所有解,而分支限界法的求解標的則是找出滿足約束條件的一個解,或是在滿足約束條件的解中找出在某種意義下的最優解。 (2)搜尋方式的不同:回溯法以深度優先的方式搜尋解空間樹,而分支限界法則以廣度優先或以最小耗費優先的方式搜尋解空間樹。
分支限界法的基本思想
分支限界法常以廣度優先或以最小耗費(最大效益)優先的方式搜尋問題的解空間樹。在分支限界法中,每一個活結點只有一次機會成為擴充套件結點。活結點一旦成為擴充套件結點,就一次性產生其所有兒子結點。在這些兒子結點中,導致不可行解或導致非最優解的兒子結點被捨棄,其餘兒子結點被加入活結點表中。 此後,從活結點表中取下一結點成為當前擴充套件結點,並重覆上述結點擴充套件過程。這個過程一直持續到找到所需的解或活結點表為空時為止。
常見的兩種分支限界法
(1)佇列式(FIFO)分支限界法 按照佇列先進先出(FIFO)原則選取下一個結點為擴充套件結點。 (2)優先佇列式分支限界法 按照優先佇列中規定的優先順序選取優先順序最高的結點成為當前擴充套件結點。
一、單源最短路徑問題
1、問題描述
在下圖所給的有向圖G中,每一邊都有一個非負邊權。要求圖G的從源頂點s到標的頂點t之間的最短路徑。

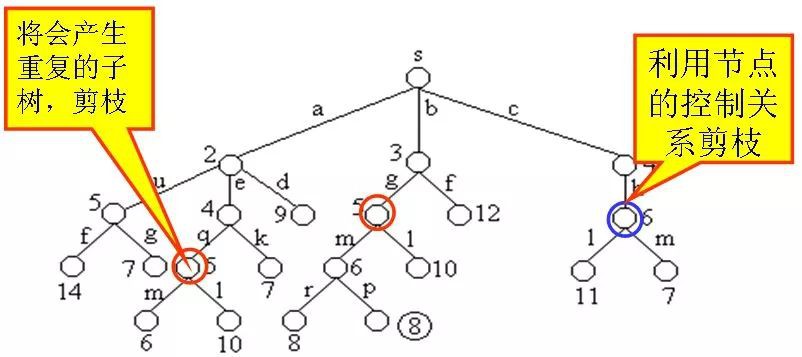
下圖是用優先佇列式分支限界法解有向圖G的單源最短路徑問題產生的解空間樹。其中,每一個結點旁邊的數字表示該結點所對應的當前路長。

找到一條路徑:
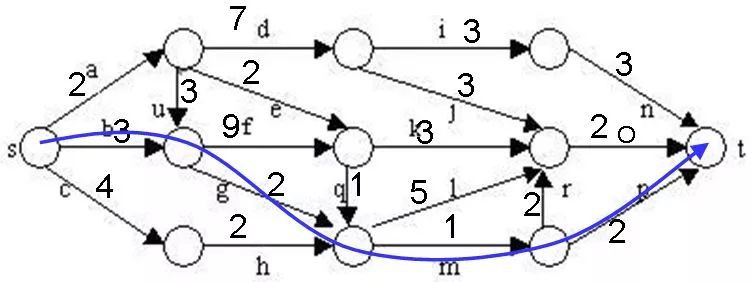
目前的最短路徑是8,一旦發現某個結點的下界不小於這個最短路進,則剪枝:

同一個結點選擇最短的到達路徑:
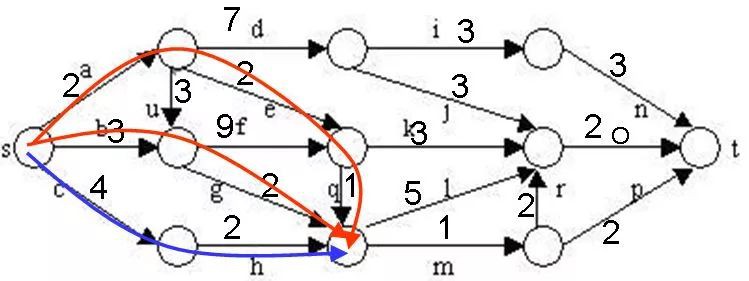
2.剪枝策略
在演演算法擴充套件結點的過程中,一旦發現一個結點的下界不小於當前找到的最短路長,則演演算法剪去以該結點為根的子樹。
在演演算法中,利用結點間的控制關係進行剪枝。從源頂點s出發,2條不同路徑到達圖G的同一頂點。由於兩條路徑的路長不同,因此可以將路長長的路徑所對應的樹中的結點為根的子樹剪去。
3.演演算法思想
解單源最短路徑問題的優先佇列式分支限界法用一極小堆來儲存活結點表。其優先順序是結點所對應的當前路長。
演演算法從圖G的源頂點s和空優先佇列開始。結點s被擴充套件後,它的兒子結點被依次插入堆中。此後,演演算法從堆中取出具有最小當前路長的結點作為當前擴充套件結點,並依次檢查與當前擴充套件結點相鄰的所有頂點。如果從當前擴充套件結點i到頂點j有邊可達,且從源出發,途經頂點i再到頂點j的所相應的路徑的長度小於當前最優路徑長度,則將該頂點作為活結點插入到活結點優先佇列中。這個結點的擴充套件過程一直繼續到活結點優先佇列為空時為止。
實現
* 作者:chinazhangjie
* 郵箱:chinajiezhang@gmail.com
* 開發語言:C++
* 開發環境:Mircosoft Virsual Studio 2008
* 時間: 2010.11.01
*/
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
struct node_info
{
public:
node_info (int i,int w)
: index (i), weight (w) {}
node_info ()
: index(0),weight(0) {}
node_info (const node_info & ni)
: index (ni.index), weight (ni.weight) {}
friend
bool operator < (const node_info& lth,const node_info& rth) {
return lth.weight > rth.weight ; // 為了實現從小到大的順序
}
public:
int index; // 結點位置
int weight; // 權值
};
struct path_info
{
public:
path_info ()
: front_index(0), weight (numeric_limits<int>::max()) {}
public:
int front_index;
int weight;
};
// single source shortest paths
class ss_shortest_paths
{
public:
ss_shortest_paths (const vector<vector<int> >& g,int end_location)
:no_edge (–1), end_node (end_location), node_count (g.size()) , graph (g)
{}
// 列印最短路徑
void print_spaths () const {
cout << “min weight : “ << shortest_path << endl;
cout << “path: “ ;
copy (s_path_index.rbegin(),s_path_index.rend(),
ostream_iterator<int> (cout, ” “));
cout << endl;
}
// 求最短路徑
void shortest_paths () {
vector<path_info> path(node_count);
priority_queue<node_info,vector<node_info> > min_heap;
min_heap.push (node_info(0,0)); // 將起始結點入隊
while (true) {
node_info top = min_heap.top (); // 取出最大值
min_heap.pop ();
// 已到達目的結點
if (top.index == end_node) {
break ;
}
// 未到達則遍歷
for (int i = 0; i < node_count; ++ i) {
// 頂點top.index和i間有邊,且此路徑長小於原先從原點到i的路徑長
if (graph[top.index][i] != no_edge &&
(top.weight + graph[top.index][i]) < path[i].weight) {
min_heap.push (node_info (i,top.weight + graph[top.index][i]));
path[i].front_index = top.index;
path[i].weight = top.weight + graph[top.index][i];
}
}
if (min_heap.empty()) {
break ;
}
}
shortest_path = path[end_node].weight;
int index = end_node;
s_path_index.push_back(index) ;
while (true) {
index = path[index].front_index ;
s_path_index.push_back(index);
if (index == 0) {
break;
}
}
}
private:
vector<vector<int> > graph ; // 圖的陣列表示
int node_count; // 結點個數
const int no_edge; // 無通路
const int end_node; // 目的結點
vector<int> s_path_index; // 最短路徑
int shortest_path; // 最短路徑
};
int main()
{
const int size = 11;
vector<vector<int> > graph (size);
for (int i = 0;i < size; ++ i) {
graph[i].resize (size);
}
for (int i = 0;i < size; ++ i) {
for (int j = 0;j < size; ++ j) {
graph[i][j] = –1;
}
}
graph[0][1] = 2;
graph[0][2] = 3;
graph[0][3] = 4;
graph[1][2] = 3;
graph[1][5] = 2;
graph[1][4] = 7;
graph[2][5] = 9;
graph[2][6] = 2;
graph[3][6] = 2;
graph[4][7] = 3;
graph[4][8] = 3;
graph[5][6] = 1;
graph[5][8] = 3;
graph[6][9] = 1;
graph[6][8] = 5;
graph[7][10] = 3;
graph[8][10] = 2;
graph[9][8] = 2;
graph[9][10] = 2;
ss_shortest_paths ssp (graph, 10);
ssp.shortest_paths ();
ssp.print_spaths ();
return 0;
}
測試資料(圖)

測試結果
min weight : 8
path: 0 2 6 9 10
覺得本文有幫助?請分享給更多人
關註「演演算法愛好者」,修煉程式設計內功

 知識星球
知識星球