netty4之後,netty中加入了記憶體池管理,看了netty後突然對這塊很感興趣,怎麼辦?最簡單的方式無非看原始碼唄。我們順著思路強行分析一波。分析下簡單需求,為了能夠簡單的操作記憶體,必須保證每次分配到的記憶體時連續的。我們來看下netty的poolChunk。
PoolChunk
該類主要負責記憶體塊的分配與回收,我們可以從原始碼中給的註釋差不多看清PoolChunk的資料結構與演演算法。先介紹兩個術語:
page-是可以分配的記憶體塊的最小單位
chunk-是一堆page的集合
下麵是chunk的構造方法
-
PoolChunk(PoolArena
arena, T memory, int pageSize, int maxOrder, int pageShifts, int chunkSize, int offset) { -
unpooled = false;
-
this.arena = arena;
-
// memory是一個容量為chunkSize的byte[](heap方式)或ByteBuffer(direct方式)
-
this.memory = memory;
-
// 每個page的大小,預設為8192,8k
-
this.pageSize = pageSize;
-
// 13
-
this.pageShifts = pageShifts;
-
// 11層
-
this.maxOrder = maxOrder;
-
// 8k * 2048
-
this.chunkSize = chunkSize;
-
this.offset = offset;
-
unusable = (byte) (maxOrder + 1);
-
log2ChunkSize = log2(chunkSize);
-
// -8192
-
subpageOverflowMask = ~(pageSize – 1);
-
freeBytes = chunkSize;
-
-
assert maxOrder 30 : “maxOrder should be + maxOrder;
-
maxSubpageAllocs = 1 <
-
-
// Generate the memory map.
-
memoryMap = new byte[maxSubpageAllocs <1];
-
depthMap = new byte[memoryMap.length];
-
int memoryMapIndex = 1;
-
for (int d = 0; d <= maxOrder; ++ d) { // move down the tree one level at a time
-
int depth = 1 <
-
for (int p = 0; p
-
// in each level traverse left to right and set value to the depth of subtree
-
memoryMap[memoryMapIndex] = (byte) d;
-
depthMap[memoryMapIndex] = (byte) d;
-
memoryMapIndex ++;
-
}
-
}
-
-
subpages = newSubpageArray(maxSubpageAllocs);
-
}
可能光看構造我們會摸不清頭腦,我去網上挖了張圖,方便大家理解。

Netty中PoolChunk內部維護一棵滿平衡二叉樹memoryMap,所有子節點管理的記憶體也屬於其父節點。這麼理解,chunk是真正分配記憶體的空間,它裡面的page就是最小可分配的單元,我們發現平衡二叉樹的葉子節點(11層)與page一一對應,再往上走,比如1024節點,它指向2048跟2049,那無非1024節點指向了page0跟page1兩個儲存單元。我們繼續看下圖
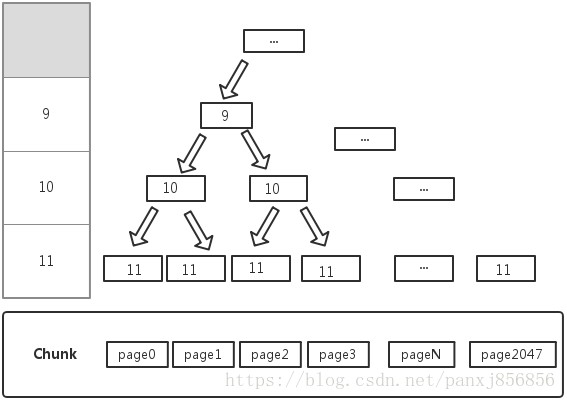
這圖跟上圖的區別無非把節點的id換成了層數。其實完全二叉樹天生就可以用陣列來表示,於是id跟層數對應起來可以用陣列memoryMap表示。陣列下標為id,值為層數。depthMap也是這樣存的,但它初始化後資料不變了,僅僅查表作用。poolChunk維護memoryMap主要用來標記使用情況。
-
1) memoryMap[id] = depth_of_id => it is free / unallocated
-
* 2) memoryMap[id] > depth_of_id => at least one of its child nodes is allocated, so we cannot allocate it, but
-
* some of its children can still be allocated based on their availability
-
* 3) memoryMap[id] = maxOrder + 1 => the node is fully allocated & thus none of its children can be allocated, it
-
* is thus marked as unusable
順便舉個例子吧,我們看下id為512的節點,它層數為9,此時memoryMap[512]=9,說明512節點下麵的page一個都沒分配,如果此時我們分配了一塊page1(隨便抽的),那麼按照演演算法,memoryMap[2049]=12,memoryMap[1024]=11,memoryMap[512]=10。一直更新上去。後面會具體從程式碼層面分析。
道理講了這麼多,看程式碼吧。建構式之前都是簡單賦值,大小我也註釋都標上了,我們看下下麵這塊程式碼,其實邏輯也很簡單,無非初始化memoryMap跟depthMap,此時可以註意到memoryMap的第一個節點即memoryMap[0]=0,這個元素是空出來的,下標為1的元素才是代表第一個節點,這樣也有好處,下標為i的父元素的左孩子就是2*i(i<<1),右孩子呢? 2*i+1 ((i<<1)^1)。位運算效率總是討人喜歡的。
-
memoryMap = new byte[maxSubpageAllocs <1];
-
depthMap = new byte[memoryMap.length];
-
int memoryMapIndex = 1;
-
for (int d = 0; d <= maxOrder; ++ d) { // move down the tree one level at a time
-
int depth = 1 <
-
for (int p = 0; p
-
// in each level traverse left to right and set value to the depth of subtree
-
memoryMap[memoryMapIndex] = (byte) d;
-
depthMap[memoryMapIndex] = (byte) d;
-
memoryMapIndex ++;
-
}
-
}
-
-
subpages = newSubpageArray(maxSubpageAllocs);
最後無非賦初值subpages。
poolChunk的資料結構差不多說清楚了,具體來看下如何向PoolChunk申請空間的
allocate()函式
-
long allocate(int normCapacity) {
-
if ((normCapacity & subpageOverflowMask) != 0) {
-
return allocateRun(normCapacity);
-
} else {
-
return allocateSubpage(normCapacity);
-
}
-
}
一開始的位運算就用的很討人喜歡,(normCapacity & subpageOverflowMask) != 0,normCapacity無非是申請空間的位元組數大小,我們可以從建構式中看到 subpageOverflowMask = ~(pageSize – 1); 那麼subpageOverflowMask大小為-8192(光看數值看不出所以然,它在記憶體中是最高位跟低13位全為0,剩下全為1)那麼很容易想到,這句話意思無非等價於normCapacity >= pageSize;
然後分兩種情況,當申請大小大於pageSize,那麼一塊page肯定不夠,於是需要多塊,傳回的是可分配normCapacity大小的節點的id;第二中情況,一個page已經夠分了,但是實際應用中會存在很多小塊記憶體的分配,如果小塊記憶體也佔用一個page明顯浪費,於是page也可以繼續拆分了,這是後話。我們先來看下allocateRun()
-
private long allocateRun(int normCapacity) {
-
int d = maxOrder – (log2(normCapacity) – pageShifts);
-
int id = allocateNode(d);
-
if (id 0) {
-
return id;
-
}
-
freeBytes -= runLength(id);
-
return id;
-
}
d表示申請normCapacity大小對應的節點的深度,透過很簡單的運算即(normCapacity/8k)再取對數,拿maxOrder(11)減一下。
-
private long allocateRun(int normCapacity) {
-
int d = maxOrder – (log2(normCapacity) – pageShifts);
-
int id = allocateNode(d);
-
if (id 0) {
-
return id;
-
}
-
freeBytes -= runLength(id);
-
return id;
-
}
d表示申請normCapacity大小對應的節點的深度,透過很簡單的運算即(normCapacity/8k)再取對數,拿maxOrder(11)減一下。
-
private int allocateNode(int d) {
-
int id = 1;
-
int initial = – (1 <// has last d bits = 0 and rest all = 1
-
byte val = value(id);
-
if (val > d) { // unusable
-
return –1;
-
}
-
while (val 0) { // id & initial == 1 <
-
id <<= 1;
-
val = value(id);
-
if (val > d) {
-
id ^= 1;
-
val = value(id);
-
}
-
}
-
byte value = value(id);
-
assert value == d && (id & initial) == 1 <“val = %d, id & initial = %d, d = %d”,
-
value, id & initial, d);
-
setValue(id, unusable); // mark as unusable
-
updateParentsAlloc(id);
-
return id;
-
}
id賦初值為1,從根節點開始找,如果(val > d)第一層的節點的值大於d,表示d層及以上都不可分配,說明當前Chunk取不出那麼大的空間,此次分配失敗。一直在樹上找直到找到與d恰好匹配的節點,即高度不小於d並且最小可分配,id<<=1往下一層走;當前節點對應大小不夠分配,則id^=1切換到父節點的另一子節點中(若父節點夠分配,則此節點肯定能分配);找到對應節點id後,把當前節點的值設為不可用,並且遞迴迴圈調整父節點的MemoryMap的值
-
private void updateParentsAlloc(int id) {
-
while (id > 1) {
-
int parentId = id >>> 1;
-
byte val1 = value(id);
-
byte val2 = value(id ^ 1);
-
byte val = val1
-
setValue(parentId, val);
-
id = parentId;
-
}
-
}
程式碼邏輯很簡單,父節點值設為子節點中的最小值。直到根節點,調整結束。
我們再看當申請大小小於pageSize的第二種情況:
-
private long allocateSubpage(int normCapacity) {
-
// Obtain the head of the PoolSubPage pool that is owned by the PoolArena and synchronize on it.
-
// This is need as we may add it back and so alter the linked-list structure.
-
PoolSubpage
head = arena.findSubpagePoolHead(normCapacity); -
synchronized (head) {
-
int d = maxOrder; // subpages are only be allocated from pages i.e., leaves
-
int id = allocateNode(d);
-
if (id 0) {
-
return id;
-
}
-
-
final PoolSubpage
[] subpages = this.subpages; -
final int pageSize = this.pageSize;
-
-
freeBytes -= pageSize;
-
-
int subpageIdx = subpageIdx(id);
-
PoolSubpage
subpage = subpages[subpageIdx]; -
if (subpage == null) {
-
subpage = new PoolSubpage
(head, this, id, runOffset(id), pageSize, normCapacity); -
subpages[subpageIdx] = subpage;
-
} else {
-
subpage.init(head, normCapacity);
-
}
-
return subpage.allocate();
-
}
-
}
針對這種情況,可以將8K的page拆成更小的塊,這已經超出chunk的管理範圍了,這個時候就出現了PoolSubpage, 透過normCapacity大小找到對應的PoolSubpage頭結點,然後加鎖(分配過程會改變連結串列結構),d=maxOrder,因此此時只需一塊page足夠,所以d直接設定為maxOrder即葉子節點就ok,透過allcNode()分配到節點的id,如果id小於0表示分配失敗(葉子節點分配完了)傳回。之後找到最高的合適節點後,開始新建(並加入到poolChunk的subpages陣列中)或初始化subpage,然後呼叫subpage的allocate()申請空間,傳回了個handle;下一篇博文會將subpage的具體邏輯。
我們再來看下釋放空間,free()函式。
-
void free(long handle) {
-
int memoryMapIdx = memoryMapIdx(handle);
-
int bitmapIdx = bitmapIdx(handle);
-
-
if (bitmapIdx != 0) { // free a subpage
-
PoolSubpage
subpage = subpages[subpageIdx(memoryMapIdx)]; -
assert subpage != null && subpage.doNotDestroy;
-
-
// Obtain the head of the PoolSubPage pool that is owned by the PoolArena and synchronize on it.
-
// This is need as we may add it back and so alter the linked-list structure.
-
PoolSubpage
head = arena.findSubpagePoolHead(subpage.elemSize); -
synchronized (head) {
-
if (subpage.free(head, bitmapIdx & 0x3FFFFFFF)) {
-
return;
-
}
-
}
-
}
-
freeBytes += runLength(memoryMapIdx);
-
setValue(memoryMapIdx, depth(memoryMapIdx));
-
updateParentsFree(memoryMapIdx);
-
}
其中傳入的handle無非是allocate得到的handle,透過handle得到page的id,如果透過handle計算得到的bitmapIdx為0,則表示是之前申請空間的第一種條件,大小大於pageSize,於是直接釋放整個節點對應的page空間,則將其memoryMap[id]=其對應的層數(depth[id]),於是調整父親節點,此時是申請時的逆過程。
-
private void updateParentsFree(int id) {
-
int logChild = depth(id) + 1;
-
while (id > 1) {
-
int parentId = id >>> 1;
-
byte val1 = value(id);
-
byte val2 = value(id ^ 1);
-
logChild -= 1; // in first iteration equals log, subsequently reduce 1 from logChild as we traverse up
-
-
if (val1 == logChild && val2 == logChild) {
-
setValue(parentId, (byte) (logChild – 1));
-
} else {
-
byte val = val1
-
setValue(parentId, val);
-
}
-
-
id = parentId;
-
}
-
}
如果左右孩子value值一樣,則父節點value設為孩子的value-1,否則設為孩子節點的最小值。
第二種情況,則需釋放subpage再繼續上面介紹的釋放page。
-
if (bitmapIdx != 0) { // free a subpage
-
PoolSubpage
subpage = subpages[subpageIdx(memoryMapIdx)]; -
assert subpage != null && subpage.doNotDestroy;
-
-
// Obtain the head of the PoolSubPage pool that is owned by the PoolArena and synchronize on it.
-
// This is need as we may add it back and so alter the linked-list structure.
-
PoolSubpage
head = arena.findSubpagePoolHead(subpage.elemSize); -
synchronized (head) {
-
if (subpage.free(head, bitmapIdx & 0x3FFFFFFF)) {
-
return;
-
}
-
}
-
}
這兒有涉及到subpage部分不是講得很清,沒關係,以poolChunk為netty記憶體池的切入點。接下來會,向下細挖subpage,向上探索poolArea等等。
 知識星球
知識星球