
-
資料庫容器化作為下一代資料庫基礎架構
-
基於編排架構管理容器化資料庫
-
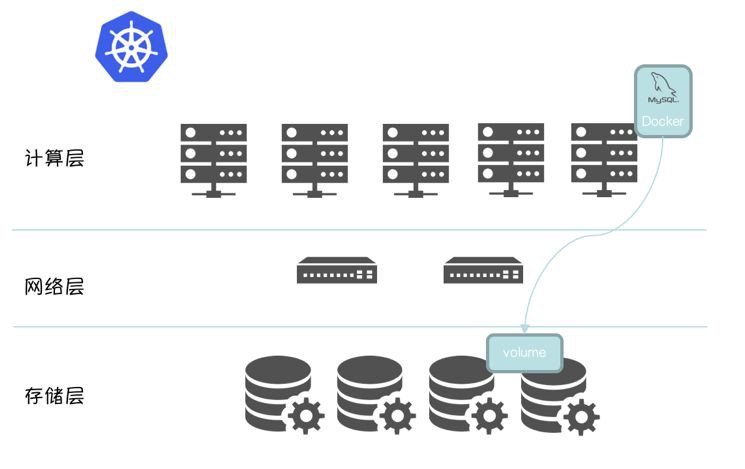
採用計算儲存分離架構

-
計算資源 / 儲存資源獨立擴充套件,架構更清晰,部署更容易。
-
將有狀態的資料下沉到儲存層,Scheduler 排程時,無需感知計算節點的儲存介質,只需排程到滿足計算資源要求的 Node,資料庫實體啟動時,只需在分散式檔案系統掛載 mapping volume 即可,可以顯著的提高資料庫實體的部署密度和計算資源利用率。
-
離線(ODPS)以機械磁碟為主
-
線上以 SSD / Flash 為主

-
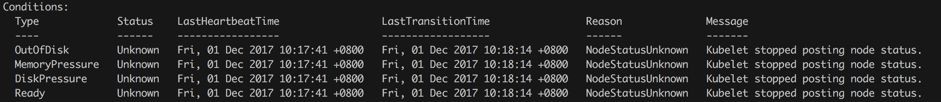
Kubelet 藉助 API Server 定期(node-status-update-frequency)更新 etcd 中對應節點的心跳資訊。
-
Controller Manager 中的 Node Controller 元件定期(node-monitor-period)輪詢 ETCD 中節點的心跳資訊。
-
如果在週期(node-monitor-grace-period)內,心跳更新丟失,該節點標記為Unknown(ConditionUnknown)。
-
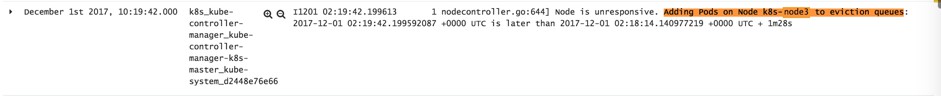
如果在週期(pod-eviction-timeout)內,心跳更新持續丟失,Node Controller 將會觸發叢集層面的驅逐機制。
-
Scheduler將Unknown節點上的所有資料庫實體排程到其他健康(Ready)節點。

-
ETCD 基於 Raft 演演算法實現。
-
Raft 演演算法是一種基於訊息傳遞(state machine replicated)且具有高度容錯(fault tolerance)特性的一致性演演算法(consensus algorithm)。
-
Raft 是大名鼎鼎的 Paxos 的簡化版本。
-
如果對於 Raft 演演算法的實現有興趣,可以看看 https://github.com/goraft/raft。

-
使用 Statefulset 建立 MySQL 單實體 gxr-oracle-statefulset(這是一個 Oracle DBA 取的名字,請原諒他)
-
Scheduler 將 MySQL 單實體排程到叢集中的節點 “k8s-node3”
-
透過 sysbench 對該實體製造極高的負載,“k8s-node3” load 飆升,導致“k8s-node3”上的 Kubelet 無法跟 API Server 通訊,並開始報錯
-
Node Controller 啟動驅逐
-
Statefulset 發起重建
-
Scheduler 將 MySQL 實體排程到“k8s-node1”上
-
新舊 MySQL 實體訪問同一個 Volume
-
資料檔案被寫壞,新舊 MySQL 實體都報錯,並無法啟動
-
kube-controller-manager 啟動引數:

-
kubelet 啟動引數:


if kl.kubeClient != nil {
// Start syncing node status immediately, this may set up things the runtime needs to run.
go wait.Until(kl.syncNodeStatus, kl.nodeStatusUpdateFrequency, wait.NeverStop)
}
obj.NodeStatusUpdateFrequency = metav1.Duration{Duration: 10 * time.Second}
func (kl *Kubelet) defaultNodeStatusFuncs() []func(*v1.Node) error {
// initial set of node status update handlers, can be modified by Option's
withoutError := func(f func(*v1.Node)) func(*v1.Node) error {
return func(n *v1.Node) error {
f(n)
return nil
}
}
return []func(*v1.Node) error{
kl.setNodeAddress,
withoutError(kl.setNodeStatusInfo),
withoutError(kl.setNodeOODCondition),
withoutError(kl.setNodeMemoryPressureCondition),
withoutError(kl.setNodeDiskPressureCondition),
withoutError(kl.setNodeReadyCondition),
withoutError(kl.setNodeVolumesInUseStatus),
withoutError(kl.recordNodeSchedulableEvent),
}
}






// Incorporate the results of node status pushed from kubelet to master.
go wait.Until(func() {
if err := nc.monitorNodeStatus(); err != nil {
glog.Errorf("Error monitoring node status: %v", err)
}
}, nc.nodeMonitorPeriod, wait.NeverStop)
NodeMonitorPeriod: metav1.Duration{Duration: 5 * time.Second},
if nc.now().After(savedNodeStatus.probeTimestamp.Add(gracePeriod)) {
// NodeReady condition was last set longer ago than gracePeriod, so update it to Unknown
// (regardless of its current value) in the master.
if currentReadyCondition == nil {
glog.V(2).Infof("node %v is never updated by kubelet", node.Name)
node.Status.Conditions = append(node.Status.Conditions, v1.NodeCondition{
Type: v1.NodeReady,
Status: v1.ConditionUnknown,
Reason: "NodeStatusNeverUpdated",
Message: fmt.Sprintf("Kubelet never posted node status."),
LastHeartbeatTime: node.CreationTimestamp,
LastTransitionTime: nc.now(),
})
} else {
glog.V(4).Infof("node %v hasn't been updated for %+v. Last ready condition is: %+v",
node.Name, nc.now().Time.Sub(savedNodeStatus.probeTimestamp.Time), observedReadyCondition)
if observedReadyCondition.Status != v1.ConditionUnknown {
currentReadyCondition.Status = v1.ConditionUnknown
currentReadyCondition.Reason = "NodeStatusUnknown"
currentReadyCondition.Message = "Kubelet stopped posting node status."
// LastProbeTime is the last time we heard from kubelet.
currentReadyCondition.LastHeartbeatTime = observedReadyCondition.LastHeartbeatTime
currentReadyCondition.LastTransitionTime = nc.now()
}
}
if observedReadyCondition.Status == v1.ConditionUnknown {
if nc.useTaintBasedEvictions {
// We want to update the taint straight away if Node is already tainted with the UnreachableTaint
if taintutils.TaintExists(node.Spec.Taints, NotReadyTaintTemplate) {
taintToAdd := *UnreachableTaintTemplate
if !util.SwapNodeControllerTaint(nc.kubeClient, []*v1.Taint{&taintToAdd;}, []*v1.Taint{NotReadyTaintTemplate}, node) {
glog.Errorf("Failed to instantly swap UnreachableTaint to NotReadyTaint. Will try again in the next cycle.")
}
} else if nc.markNodeForTainting(node) {
glog.V(2).Infof("Node %v is unresponsive as of %v. Adding it to the Taint queue.",
node.Name,
decisionTimestamp,
)
}
} else {
if decisionTimestamp.After(nc.nodeStatusMap[node.Name].probeTimestamp.Add(nc.podEvictionTimeout)) {
if nc.evictPods(node) {
glog.V(2).Infof("Node is unresponsive. Adding Pods on Node %s to eviction queues: %v is later than %v + %v",
node.Name,
decisionTimestamp,
nc.nodeStatusMap[node.Name].readyTransitionTimestamp,
nc.podEvictionTimeout-gracePeriod,
)
}
}
}
}
// evictPods queues an eviction for the provided node name, and returns false if the node is already
// queued for eviction.
func (nc *Controller) evictPods(node *v1.Node) bool {
nc.evictorLock.Lock()
defer nc.evictorLock.Unlock()
return nc.zonePodEvictor[utilnode.GetZoneKey(node)].Add(node.Name, string(node.UID))
}



if nc.useTaintBasedEvictions {
// Handling taint based evictions. Because we don't want a dedicated logic in TaintManager for NC-originated
// taints and we normally don't rate limit evictions caused by taints, we need to rate limit adding taints.
go wait.Until(nc.doNoExecuteTaintingPass, scheduler.NodeEvictionPeriod, wait.NeverStop)
} else {
// Managing eviction of nodes:
// When we delete pods off a node, if the node was not empty at the time we then
// queue an eviction watcher. If we hit an error, retry deletion.
go wait.Until(nc.doEvictionPass, scheduler.NodeEvictionPeriod, wait.NeverStop)
}
func (nc *Controller) doEvictionPass() {
nc.evictorLock.Lock()
defer nc.evictorLock.Unlock()
for k := range nc.zonePodEvictor {
// Function should return 'false' and a time after which it should be retried, or 'true' if it shouldn't (it succeeded).
nc.zonePodEvictor[k].Try(func(value scheduler.TimedValue) (bool, time.Duration) {
node, err := nc.nodeLister.Get(value.Value)
if apierrors.IsNotFound(err) {
glog.Warningf("Node %v no longer present in nodeLister!", value.Value)
} else if err != nil {
glog.Warningf("Failed to get Node %v from the nodeLister: %v", value.Value, err)
} else {
zone := utilnode.GetZoneKey(node)
evictionsNumber.WithLabelValues(zone).Inc()
}
nodeUID, _ := value.UID.(string)
remaining, err := util.DeletePods(nc.kubeClient, nc.recorder, value.Value, nodeUID, nc.daemonSetStore)
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("unable to evict node %q: %v", value.Value, err))
return false, 0
}
if remaining {
glog.Infof("Pods awaiting deletion due to Controller eviction")
}
return true, 0
})
}
}


2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] mysqld (mysqld 5.7.19-log) starting as process 963 ...
2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB: PUNCH HOLE support available
2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB: Mutexes and rw_locks use GCC atomic builtins
2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB: Uses event mutexes
2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB: GCC builtin __atomic_thread_fence() is used for memory barrier
2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB: Compressed tables use zlib 1.2.3
2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB: Using Linux native AIO
2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB: Number of pools: 1
2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB: Using CPU crc32 instructions
2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB: Initializing buffer pool, total size = 3.25G, instances = 2, chunk size = 128M
2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB: Completed initialization of buffer pool
2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB: If the mysqld execution user is authorized, page cleaner thread priority can be changed. See the man page of setpriority().
2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB: Highest supported file format is Barracuda.
2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB: Log scan progressed past the checkpoint lsn 406822323
2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB: Doing recovery: scanned up to log sequence number 406823190
2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB: Database was not shutdown normally!
2017-12-01 10:19:47 5628 [Note] InnoDB: Starting crash recovery.
2017-12-01 10:19:47 5669 [Note] InnoDB: Starting an apply batch of log records to the database...
InnoDB: Progress in percent: 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99
2017-12-01 10:19:47 5669 [Note] InnoDB: Apply batch completed
2017-12-01 10:19:47 5669 [Note] InnoDB: Last MySQL binlog file position 0 428730, file name mysql-bin.000004
2017-12-01 10:19:47 5669 [Note] InnoDB: Removed temporary tablespace data file: "ibtmp1"
2017-12-01 10:19:47 5669 [Note] InnoDB: Creating shared tablespace for temporary tables
2017-12-01 10:19:47 5669 [Note] InnoDB: Setting file './ibtmp1' size to 12 MB. Physically writing the file full; Please wait ...
2017-12-01 10:19:47 5669 [Note] InnoDB: File './ibtmp1' size is now 12 MB.
2017-12-01 10:19:47 5669 [Note] InnoDB: 96 redo rollback segment(s) found. 96 redo rollback segment(s) are active.
2017-12-01 10:19:47 5669 [Note] InnoDB: 32 non-redo rollback segment(s) are active.
2017-12-01 10:19:47 5669 [Note] InnoDB: Waiting for purge to start
2017-12-01 10:19:47 0x7fcb08928700 InnoDB: Assertion failure in thread 140509998909184 in file trx0purge.cc line 168
InnoDB: Failing assertion: purge_sys->iter.trx_no <= purge_sys->rseg->last_trx_no
InnoDB: We intentionally generate a memory trap.
InnoDB: Submit a detailed bug report to http://bugs.mysql.com.
InnoDB: If you get repeated assertion failures or crashes, even
InnoDB: immediately after the mysqld startup, there may be
InnoDB: corruption in the InnoDB tablespace. Please refer to
InnoDB: http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/forcing-innodb-recovery.html
InnoDB: about forcing recovery.
10:19:47 5669 - mysqld got signal 6 ;


 知識星球
知識星球