- 繼承 MessageSource,提供國際化的標準訪問策略。
- 繼承 ApplicationEventPublisher ,提供強大的事件機制。
- 擴充套件 ResourceLoader,可以用來載入多個 Resource,可以靈活訪問不同的資源。
- 對 Web 應用的支援。
ApplicationContext
下圖是 ApplicationContext 結構類圖:
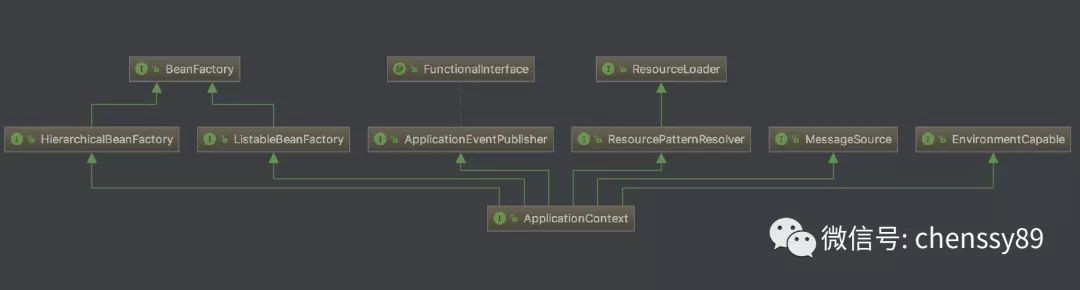
- BeanFactory:Spring 管理 Bean 的頂層介面,我們可以認為他是一個簡易版的 Spring 容器。ApplicationContext 繼承 BeanFactory 的兩個子類:HierarchicalBeanFactory 和 ListableBeanFactory。HierarchicalBeanFactory 是一個具有層級關係的 BeanFactory,擁有屬性 parentBeanFactory。ListableBeanFactory 實現了列舉方法可以列舉出當前 BeanFactory 中所有的 bean 物件而不必根據 name 一個一個的獲取。
- ApplicationEventPublisher:用於封裝事件釋出功能的介面,向事件監聽器(Listener)傳送事件訊息。
- ResourceLoader:Spring 載入資源的頂層介面,用於從一個源載入資源檔案。ApplicationContext 繼承 ResourceLoader 的子類 ResourcePatternResolver,該介面是將 location 解析為 Resource 物件的策略介面。
- MessageSource:解析 message 的策略介面,用不支撐國際化等功能。
- EnvironmentCapable:用於獲取 Environment 的介面。
ApplicationContext 的子介面
ApplicationContext 有兩個直接子類:WebApplicationContext 和 ConfigurableApplicationContext。
WebApplicationContext
public interface WebApplicationContext extends ApplicationContext {ServletContext getServletContext();}
該介面只有一個 getServletContext() ,用於給 servlet 提供背景關係資訊。
ConfigurableApplicationContext
public interface ConfigurableApplicationContext extends ApplicationContext, Lifecycle, Closeable {// 為 ApplicationContext 設定唯一 IDvoid setId(String id);// 為 ApplicationContext 設定 parent// 父類不應該被修改:如果建立的物件不可用時,則應該在建構式外部設定它void setParent(@Nullable ApplicationContext parent);// 設定 Environmentvoid setEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment);// 獲取 Environment@OverrideConfigurableEnvironment getEnvironment();// 新增 BeanFactoryPostProcessorvoid addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor);// 新增 ApplicationListenervoid addApplicationListener(ApplicationListener> listener);// 新增 ProtocolResolvervoid addProtocolResolver(ProtocolResolver resolver);// 載入或者掃清配置// 這是一個非常重要的方法void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException;// 註冊 shutdown hookvoid registerShutdownHook();// 關閉 ApplicationContext@Overridevoid close();// ApplicationContext 是否處於啟用狀態boolean isActive();// 獲取當前背景關係的 BeanFactoryConfigurableListableBeanFactory getBeanFactory() throws IllegalStateException;}
從上面程式碼可以看到 ConfigurableApplicationContext 介面提供的方法都是對 ApplicationContext 進行配置的,例如 setEnvironment()、 addBeanFactoryPostProcessor,同時它還繼承瞭如下兩個介面:
- Lifecycle:對 context 生命週期的管理,它提供
start()和stop()方法啟動和暫停元件。 - Closeable:標準 JDK 所提供的一個介面,用於最後關閉元件釋放資源等。
WebApplicationContext 介面和 ConfigurableApplicationContext 介面有一個共同的子類介面 ConfigurableWebApplicationContext,該介面將這兩個介面進行合併,提供了一個可配置、可管理、可關閉的WebApplicationContext,同時該介面還增加了 setServletContext(), setServletConfig()等方法,用於裝配WebApplicationContext。
public interface ConfigurableWebApplicationContext extends WebApplicationContext, ConfigurableApplicationContext {void setServletContext(@Nullable ServletContext servletContext);void setServletConfig(@Nullable ServletConfig servletConfig);ServletConfig getServletConfig();void setNamespace(@Nullable String namespace);String getNamespace();void setConfigLocation(String configLocation);void setConfigLocations(String... configLocations);String[] getConfigLocations();}
上面三個介面就可以構成一個比較完整的 Spring 容器,整個 Spring 容器體系涉及的介面較多,所以下麵小編就一個具體的實現類來看看 ApplicationContext 的實現(其實在前面一系列的文章中,小編對涉及的大部分介面都已經分析了其原理),當然不可能每個方法都涉及到,但小編會把其中最為重要的實現方法貼出來分析。ApplicationContext 的實現類較多,就以 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 來分析 ApplicationContext。
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 是我們在學習 Spring 過程中用的非常多的一個類,很多人第一個接觸的 Spring 容器就是它,包括小編自己,下麵程式碼我想很多人依然還記得吧。
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");StudentService studentService = (StudentService)ac.getBean("studentService");
下圖是 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 的結構類圖:
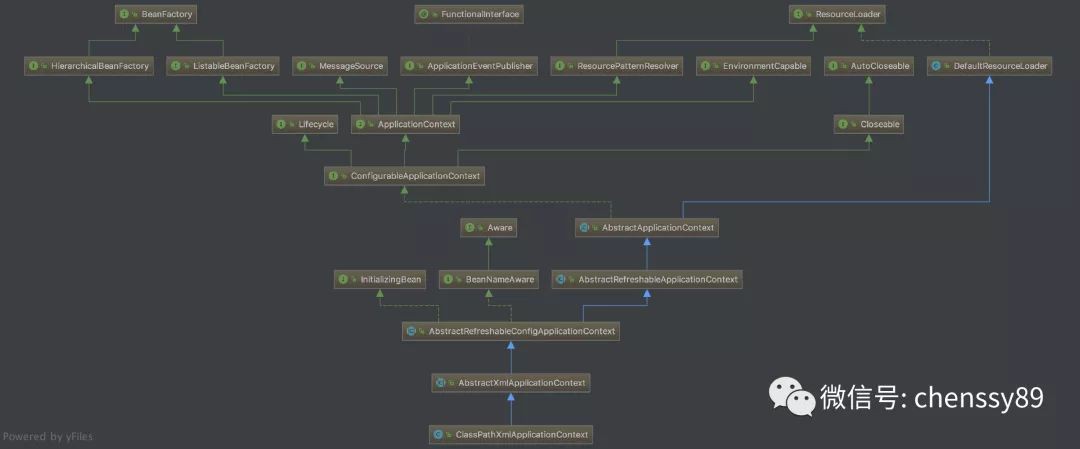
主要的的類層級關係如下:
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContextorg.springframework.context.support.AbstractRefreshableApplicationContextorg.springframework.context.support.AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContextorg.springframework.context.support.AbstractXmlApplicationContextorg.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
這種設計是模板方法樣式典型的應用,AbstractApplicationContext 實現了 ConfigurableApplicationContext 這個全家桶介面,其子類 AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext 又實現了 BeanNameAware 和 InitializingBean 介面。所以 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 設計的頂級介面有:
BeanFactory:Spring 容器 Bean 的管理MessageSource:管理 message ,實現國際化等功能ApplicationEventPublisher:事件釋出ResourcePatternResolver:資源載入EnvironmentCapable:系統 Environment(profile + Properties) 相關Lifecycle:管理生命週期Closeable:關閉,釋放資源InitializingBean:自定義初始化BeanNameAware:設定 beanName 的 Aware 介面
下麵就這些介面來一一分析。
MessageSource
MessageSource 定義了獲取 message 的策略方法 getMessage(),在 ApplicationContext 體系中,該方法 AbstractApplicationContext 實現,在 AbstractApplicationContext 中,它持有一個 MessageSource 實體,將 getMessage() 的實現給該實體來實現,如下:
private MessageSource messageSource;// 實現 getMessage()public String getMessage(String code, @Nullable Object[] args, @Nullable String defaultMessage, Locale locale) {// 委託給 messageSource 實現return getMessageSource().getMessage(code, args, defaultMessage, locale);}private MessageSource getMessageSource() throws IllegalStateException {if (this.messageSource == null) {throw new IllegalStateException("MessageSource not initialized - " +"call 'refresh' before accessing messages via the context: " + this);}return this.messageSource;}
真正實現 “ 是在 AbstractMessageSource 中,如下:
public final String getMessage(String code, @Nullable Object[] args, @Nullable String defaultMessage, Locale locale) {String msg = getMessageInternal(code, args, locale);if (msg != null) {return msg;}if (defaultMessage == null) {return getDefaultMessage(code);}return renderDefaultMessage(defaultMessage, args, locale);}
具體的實現這裡就不分析了,有興趣的小夥伴可以自己去深入研究。
ApplicationEventPublisher
用於封裝事件釋出功能的介面,向事件監聽器(Listener)傳送事件訊息。
該介面提供了一個 publishEvent() 用於通知在此應用程式中註冊的所有的監聽器。該方法在 AbstractApplicationContext 中實現。
@Overridepublic void publishEvent(Object event) {publishEvent(event, null);}protected void publishEvent(Object event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {Assert.notNull(event, "Event must not be null");if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace("Publishing event in " + getDisplayName() + ": " + event);}ApplicationEvent applicationEvent;if (event instanceof ApplicationEvent) {applicationEvent = (ApplicationEvent) event;}else {applicationEvent = new PayloadApplicationEvent<>(this, event);if (eventType == null) {eventType = ((PayloadApplicationEvent) applicationEvent).getResolvableType();}}if (this.earlyApplicationEvents != null) {this.earlyApplicationEvents.add(applicationEvent);}else {getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(applicationEvent, eventType);}if (this.parent != null) {if (this.parent instanceof AbstractApplicationContext) {((AbstractApplicationContext) this.parent).publishEvent(event, eventType);}else {this.parent.publishEvent(event);}}}
如果指定的事件不是ApplicationEvent,則它將包裝在PayloadApplicationEvent中。如果存在父級 ApplicationContext ,則同樣要將 event 釋出給父級 ApplicationContext。
ResourcePatternResolver
ResourcePatternResolver 介面繼承 ResourceLoader 介面,為將 location 解析為 Resource 物件的策略介面。他提供的 getResources() 在 AbstractApplicationContext 中實現,在 AbstractApplicationContext 中他持有一個 ResourcePatternResolver 的實體物件。
如下:
public Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException {return this.resourcePatternResolver.getResources(locationPattern);}
如果小夥伴對 Spring 的 ResourceLoader 比較熟悉的話,你會發現最終是在 PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver 中實現,該類是 ResourcePatternResolver 介面的實現者。
EnvironmentCapable
提供當前系統環境 Environment 元件。提供了一個 getEnvironment() 用於傳回 Environment 實體物件,該方法在 AbstractApplicationContext 實現。
public ConfigurableEnvironment getEnvironment() {if (this.environment == null) {this.environment = createEnvironment();}return this.environment;}
如果持有的 environment 實體物件為空,則呼叫 createEnvironment() 建立一個。
protected ConfigurableEnvironment createEnvironment() {return new StandardEnvironment();}
StandardEnvironment 是一個適用於非 WEB 應用的 Environment。
Lifecycle
一個用於管理宣告週期的介面。
在 AbstractApplicationContext 中存在一個 LifecycleProcessor 型別的實體物件 lifecycleProcessor,AbstractApplicationContext 中關於 Lifecycle 介面的實現都是委託給 lifecycleProcessor 實現的。如下:
@Overridepublic void start() {getLifecycleProcessor().start();publishEvent(new ContextStartedEvent(this));}@Overridepublic void stop() {getLifecycleProcessor().stop();publishEvent(new ContextStoppedEvent(this));}@Overridepublic boolean isRunning() {return (this.lifecycleProcessor != null && this.lifecycleProcessor.isRunning());}
在啟動、停止的時候會分別釋出 ContextStartedEvent 和 ContextStoppedEvent 事件。
Closeable
Closeable 介面用於關閉和釋放資源,提供了 close() 以釋放物件所持有的資源。在 ApplicationContext 體系中由AbstractApplicationContext 實現,用於關閉 ApplicationContext 銷毀所有 bean ,此外如果註冊有 JVM shutdown hook,同樣要將其移除。如下:
public void close() {synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {doClose();// If we registered a JVM shutdown hook, we don't need it anymore now:// We've already explicitly closed the context.if (this.shutdownHook != null) {try {Runtime.getRuntime().removeShutdownHook(this.shutdownHook);}catch (IllegalStateException ex) {// ignore - VM is already shutting down}}}}
呼叫 doClose() 釋出 ContextClosedEvent 事件,銷毀所有 bean(單例),關閉 BeanFactory 。如下:
protected void doClose() {// 省略部分程式碼try {// Publish shutdown event.publishEvent(new ContextClosedEvent(this));}catch (Throwable ex) {logger.warn("Exception thrown from ApplicationListener handling ContextClosedEvent", ex);}// 省略部分程式碼destroyBeans();closeBeanFactory();onClose();this.active.set(false);}}
InitializingBean
InitializingBean 為 bean 提供了初始化方法的方式,它提供的 afterPropertiesSet() 用於執行初始化動作。在 ApplicationContext 體系中,該方法由 AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext 實現,如下:
public void afterPropertiesSet() {if (!isActive()) {refresh();}}
執行 refresh() ,該方法在 AbstractApplicationContext 中執行,執行整個 Spring 容器的初始化過程。該方法將在下篇文章進行詳細分析說明。
BeanNameAware
設定 bean name 的介面。介面在 AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext 中實現。
public void setBeanName(String name) {if (!this.setIdCalled) {super.setId(name);setDisplayName("ApplicationContext '" + name + "'");}}
由於篇幅問題再加上大部分介面小編都已經在前面文章進行了詳細的闡述,所以本文主要是以 Spring Framework 的 ApplicationContext 為中心,對其結構和功能的實現進行了簡要的說明。這裡不得不說 Spring 真的是一個非常優秀的框架,具有良好的結構設計和介面抽象,它的每一個介面職能單一,且都是具體功能到各個模組的高度抽象,且幾乎每套介面都提供了一個預設的實現(defaultXXX)。對於 ApplicationContext 體系而言,他繼承 Spring 中眾多的核心介面,能夠為客戶端提供一個相對完整的 Spring 容器,介面 ConfigurableApplicationContext 對 ApplicationContext 介面再次進行擴充套件,提供了生命週期的管理功能。抽象類 ApplicationContext 對整套介面提供了大部分的預設實現,將其中“不易變動”的部分進行了封裝,透過“組合”的方式將“容易變動”的功能委託給其他類來實現,同時利用模板方法樣式將一些方法的實現開放出去由子類實現,從而實現“對擴充套件開放,對修改封閉”的設計原則。
最後我們再來領略下圖的風采:

 知識星球
知識星球