(點選上方公眾號,可快速關註)
來源:程式員小灰
在之前的漫畫中,我們介紹了二叉堆和堆排序。沒看過的小夥伴可以看一看前文:
這一次,我們來講一講二叉堆的另外一個應用:優先佇列


佇列的特點是什麼?
聰明的小夥伴們都知道,是先進先出(FIFO)。
入佇列:
出佇列:

那麼,優先佇列又是什麼樣子呢?
優先佇列不再遵循先入先出的原則,而是分為兩種情況:
最大優先佇列,無論入隊順序,當前最大的元素優先出隊。
最小優先佇列,無論入隊順序,當前最小的元素優先出隊。
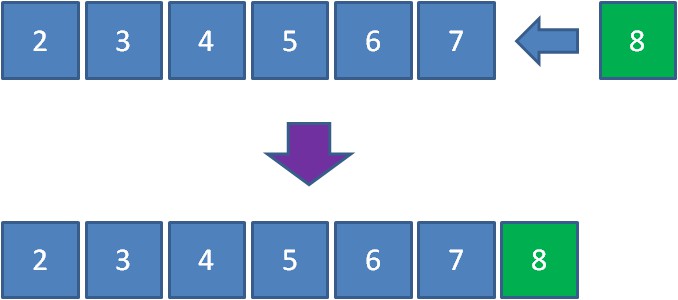
比如有一個最大優先佇列,它的最大元素是8,那麼雖然元素8並不是隊首元素,但出隊的時候仍然讓元素8首先出隊:

要滿足以上需求,利用線性資料結構並非不能實現,但是時間複雜度較高,最壞時間複雜度O(n),並不是最理想的方式。
至於為什麼最壞時間複雜度是O(n),大家可以思考下。


讓我們回顧一下二叉堆的特性:
1.最大堆的堆頂是整個堆中的最大元素
2.最小堆的堆頂是整個堆中的最小元素
因此,我們可以用最大堆來實現最大優先佇列,每一次入隊操作就是堆的插入操作,每一次出隊操作就是刪除堆頂節點。
入隊操作:
1.插入新節點5

2.新節點5上浮到合適位置。

出隊操作:
1.把原堆頂節點10“出隊”

2.最後一個節點1替換到堆頂位置

3.節點1下沉,節點9成為新堆頂



public class PriorityQueue {
private int[] array;
private int size;
public PriorityQueue(){
//佇列初始長度32
array = new int[32];
}
/**
* 入隊
* @param key 入隊元素
*/
private void enQueue(int key) {
//佇列長度超出範圍,擴容
if(size >= array.length){
resize();
}
array[size++] = key;
upAdjust();
}
/**
* 出隊
*/
private int deQueue() throws Exception {
if(size <= 0){
throw new Exception("the queue is empty !");
}
//獲取堆頂元素
int head = array[0];
//最後一個元素移動到堆頂
array[0] = array[--size];
downAdjust();
return head;
}
/**
* 上浮調整
*/
private void upAdjust() {
int childIndex = size-1;
int parentIndex = childIndex/2;
// temp儲存插入的葉子節點值,用於最後的賦值
int temp = array[childIndex];
while (childIndex > 0 && temp > array[parentIndex])
{
//無需真正交換,單向賦值即可
array[childIndex] = array[parentIndex];
childIndex = parentIndex;
parentIndex = parentIndex / 2;
}
array[childIndex] = temp;
}
/**
* 下沉調整
*/
private void downAdjust() {
// temp儲存父節點值,用於最後的賦值
int parentIndex = 0;
int temp = array[parentIndex];
int childIndex = 1;
while (childIndex < size) {
// 如果有右孩子,且右孩子大於左孩子的值,則定位到右孩子
if (childIndex + 1 < size && array[childIndex + 1] > array[childIndex]) {
childIndex++;
}
// 如果父節點大於任何一個孩子的值,直接跳出
if (temp >= array[childIndex])
break;
//無需真正交換,單向賦值即可
array[parentIndex] = array[childIndex];
parentIndex = childIndex;
childIndex = 2 * childIndex + 1;
}
array[parentIndex] = temp;
}
/**
* 下沉調整
*/
private void resize() {
//佇列容量翻倍
int newSize = this.size * 2;
this.array = Arrays.copyOf(this.array, newSize);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
PriorityQueue priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue();
priorityQueue.enQueue(3);
priorityQueue.enQueue(5);
priorityQueue.enQueue(10);
priorityQueue.enQueue(2);
priorityQueue.enQueue(7);
System.out.println("出隊元素:" + priorityQueue.deQueue());
System.out.println("出隊元素:" + priorityQueue.deQueue());
}
}
程式碼中採用陣列來儲存二叉堆的元素,因此當元素超過陣列範圍的時候,需要進行resize來擴大陣列長度。

【關於投稿】
如果大家有原創好文投稿,請直接給公號傳送留言。
① 留言格式:
【投稿】+《 文章標題》+ 文章連結
② 示例:
【投稿】《不要自稱是程式員,我十多年的 IT 職場總結》:
http://blog.jobbole.com/94148/
③ 最後請附上您的個人簡介哈~
覺得本文有幫助?請分享給更多人
關註「演演算法愛好者」,修煉程式設計內功
 知識星球
知識星球